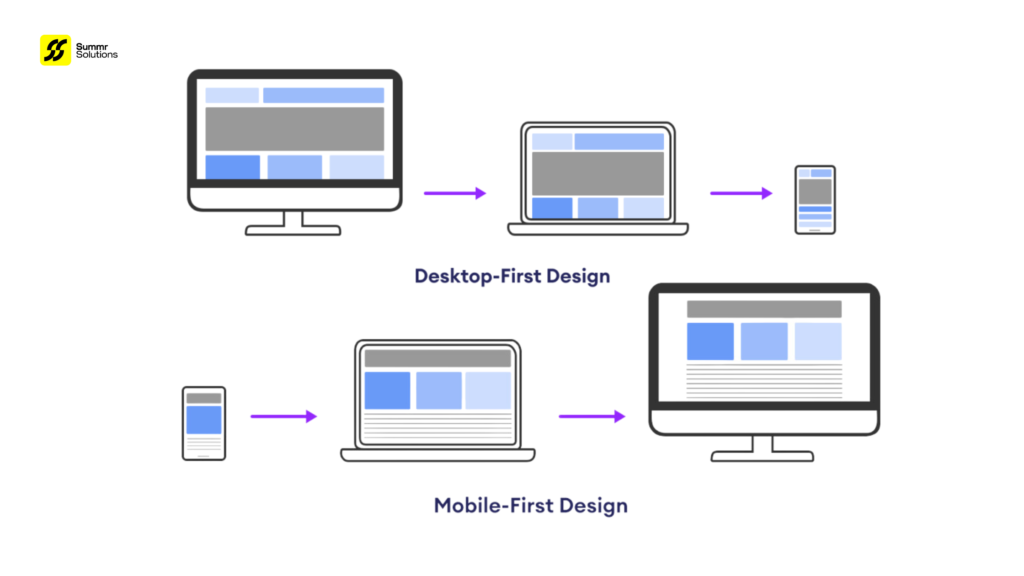
When navigating the world of content marketing, the terms “blog” and “article” are often used interchangeably. However, while both share similarities, there are distinct differences in purpose, style, and format. Understanding these differences can help you create more effective content based on your audience and objectives.
Key Differences Between Blog and Article:
| Aspect | Blog | Article |
|---|---|---|
| Tone | Conversational, informal | Formal, neutral, objective |
| Length | 500-1,500 words (can vary) | 1,000-5,000+ words |
| Purpose | To engage, entertain, inform | To inform, analyze, educate |
| Frequency | Published regularly (weekly/daily) | Published less frequently |
| Structure | Short paragraphs, bullet points, visuals | Detailed structure with logical flow |
| SEO Optimization | Highly optimized for search engines | Less focus on SEO |
| Content Style | Personal opinions, tips, advice | Research-driven, facts, and citations |
What is a Blog?
A blog refers to content typically published on a website that reflects the writer’s or brand’s perspective. Blogs are often conversational, engaging, and updated regularly to keep the audience informed or entertained. They can cover a wide range of topics, from personal reflections to industry insights.
Key Characteristics of Blogs:
- Tone:
Blogs are usually informal, friendly, and conversational. This tone makes them more accessible to a broader audience. - Length:
While there is no fixed length, blogs are often shorter than articles, ranging from 500 to 1,500 words. However, longer, in-depth blog posts (1,500+ words) are becoming more popular for SEO purposes. - Purpose:
Blogs aim to inform, entertain, or engage with readers. They often include personal opinions, anecdotes, or advice and are designed to create ongoing engagement with the audience. - Structure:
Blogs typically use a relaxed structure, with headings, bullet points, images, and short paragraphs to improve readability. Many blogs include multimedia, such as videos or infographics, to enhance the content. - SEO-Focused:
Blogs are often optimized for SEO (Search Engine Optimization) with targeted keywords, meta descriptions, and links to help improve the website’s ranking on search engines. - Frequency:
Blogs are published frequently, sometimes multiple times a week or even daily, as they are often part of a content marketing strategy.
Example:
A blog post on “Sustainable Web Design Building A Greener Online Experience” would offer quick, actionable advice in a conversational tone, designed to engage readers and encourage further exploration of the topic.
What is an Article?
An article tends to be more formal and is often associated with traditional media outlets like newspapers, magazines, and academic journals. Articles are fact-driven and tend to offer in-depth analysis or investigation into a specific topic.
Key Characteristics of Articles:
- Tone:
Articles generally have a formal, professional tone, focusing on presenting factual information rather than personal opinions. The tone is neutral and objective. - Length:
Articles are typically longer and more detailed than blog posts, often ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 words or more, depending on the subject and depth of coverage. - Purpose:
Articles aim to inform, analyze, or educate readers about a specific topic. They rely on well-researched information and often include citations or references to credible sources. - Structure:
Articles are usually structured with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. They follow a logical flow, providing detailed analysis, facts, or expert insights, making them suitable for readers looking for in-depth information. - Fact-Based:
Articles are fact-driven and often require extensive research, including interviews, statistics, and references to provide well-rounded coverage of the subject. - Publishing Frequency:
Articles tend to be published less frequently than blog posts and are often found in publications, journals, or online platforms that focus on in-depth content.
Example:
An article on “The Impact of Climate Change on Global Agriculture” would offer an in-depth analysis backed by data, expert opinions, and research, often meant to educate or inform the reader on the subject.
When to Use a Blog and Article
- Use a Blog When:
You want to engage your audience with conversational content, provide quick tips, share updates, or drive traffic to your website via SEO-friendly posts. - Use an Article When:
You need to provide in-depth analysis, factual information, or expert insights on a specific topic, especially when the goal is to educate or inform in a formal manner.
In Conclusion:
While blogs and articles both serve the purpose of sharing information, they cater to different audiences and purposes. Blogs offer a more personal, engaging approach, while articles provide in-depth, fact-driven content. Understanding the distinction allows you to choose the best format to reach and resonate with your audience effectively.